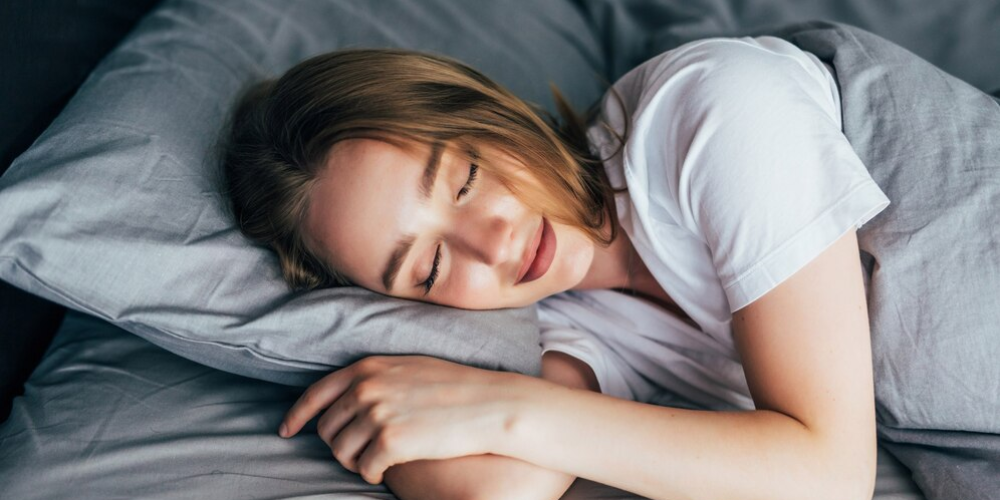
Achieving a restful night’s sleep is crucial for overall well-being, affecting energy levels, mood, and long-term health. Knowing how to sleep better can help improve concentration, strengthen immunity, and reduce the risk of chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
By adopting the following strategies, you can create an environment and routine that promotes quality sleep.
1. Bright Light Exposure During the Day
Natural light exposure during daylight hours supports your body’s internal clock, helping regulate sleep and wake cycles. Spending time outside or using a bright light therapy device can improve sleep quality and boost daytime energy. Studies show consistent exposure to natural light helps you fall asleep faster and enhances the depth of sleep at night.
2. Minimize Blue Light in the Evening
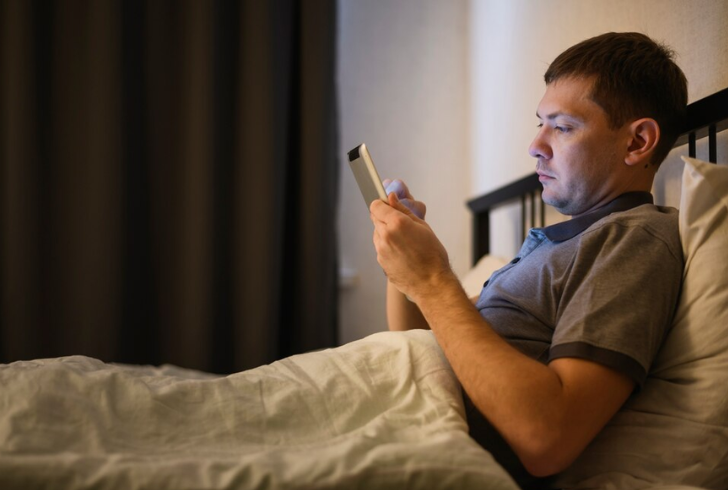

Freepik | Minimize screen time before bed with blue-light blocking glasses or night mode settings.
Excessive exposure to blue light—especially from screens—can suppress melatonin production, the hormone that helps your body prepare for sleep. Limiting screen time to two hours before bed or using blue light-blocking glasses can minimize its disruptive effects. Adjusting device settings to "night mode" is another effective step.
3. Avoid Caffeine Late in the Day
Caffeine remains in your system for several hours, potentially interfering with sleep even if consumed earlier in the day. To prevent restlessness at night, avoid coffee, energy drinks, or caffeinated teas in the late afternoon or evening. Opt for caffeine-free herbal teas or water instead.
4. Keep Daytime Naps Short and Consistent
While short naps can boost alertness, long or irregular naps may confuse your body’s sleep-wake cycle. If naps seem to interfere with your nighttime rest, consider limiting them to 20-30 minutes earlier in the day.
5. Stick to a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Irregular sleep patterns can disrupt our circadian rhythm, so try setting a fixed bedtime and wake-up time—even on weekends.
6. Melatonin Supplements
Melatonin supplements can help signal to your brain that it’s time to wind down. If sleep challenges persist, consult a healthcare professional for guidance on dosage and duration.
7. Limit Alcohol Before Bed
Though alcohol might make you feel drowsy, it can disrupt sleep cycles and decrease melatonin levels. If consumed too close to bedtime, it may lead to fragmented sleep and increase the likelihood of waking up during the night.
8. Invest in Comfortable Bedding
The quality of your mattress, pillows, and bedding plays a significant role in how well you sleep. Medium-firm mattresses often provide optimal support for most people. Additionally, consider season-appropriate materials, such as wool for cooler temperatures or linen for warmth, to enhance comfort.
9. Optimize Your Bedroom Environment
A sleep-friendly environment involves reducing noise, keeping the room dark, and maintaining a cool yet comfortable temperature, typically around 65°F. Blackout curtains, white noise machines, or fans can further improve the space for undisturbed sleep.
10. Avoid Late-Night Meals
Eating heavy or high-carb meals late at night can hinder your ability to sleep well, so opt for lighter meals.
11. Monitor Fluid Intake Before Bed
Excessive drinking before sleep can lead to frequent nighttime trips to the bathroom. Limit liquids in the evening and ensure you visit the bathroom right before bed to reduce interruptions.
12. Practice Relaxation Techniques
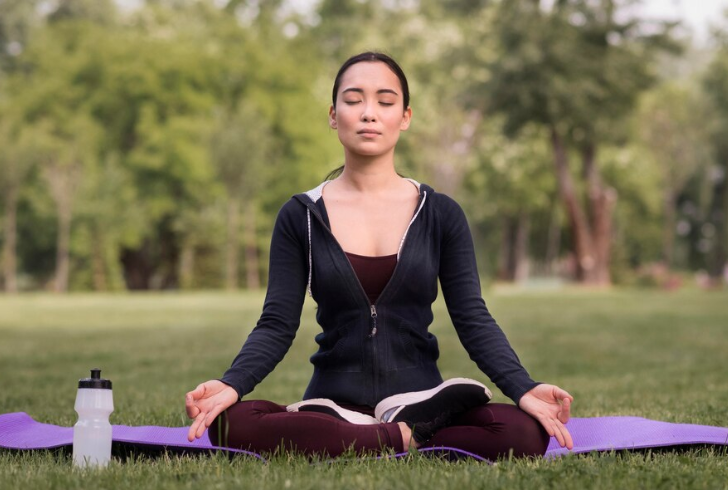

Freepik | Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can soothe the mind and body.
Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or light yoga, can calm the mind and body. Listening to soothing music or taking a warm bath may also help transition into a more relaxed state, preparing you for rest.
13. Identify and Address Sleep Disorders
Persistent sleep issues might indicate an underlying condition like sleep apnea, insomnia, or restless legs syndrome. If problems continue despite lifestyle changes, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment options.
14. Exercise Regularly, But Not Right Before Bed
This can improve sleep quality and reduce symptoms of insomnia. However, avoid intense exercise in the hours leading up to bedtime, as it may increase alertness and delay sleep onset.
Improving sleep often requires a combination of habits, environmental adjustments, and, occasionally, supplemental support. By following these 15 evidence-based tips on how to sleep better, you can pave the way for restful nights and energized days. Remember, consistent effort in cultivating healthy sleep routines is the key to long-term results.